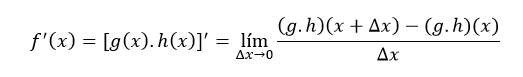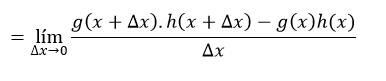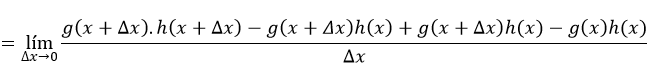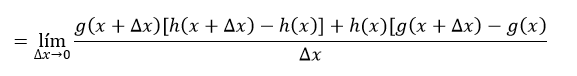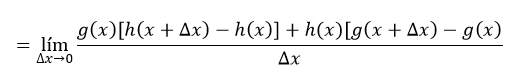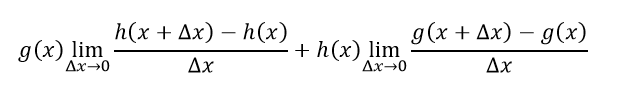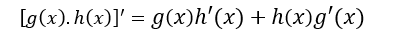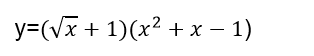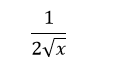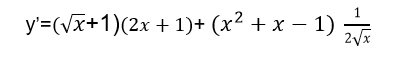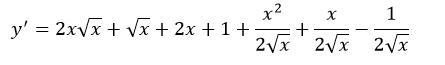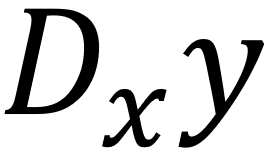
En este post queremos deducir la técnica para derivar el producto de las funciones de variable real continuas y diferenciables, g y h.
In this post we want to deduce the technique for deriving the product of the continuous and differentiable real variable functions, g and h.
Inicialmente, vamos a deducir esa técnica usando la definición formal de derivada. // Initially, let's deduce that technique using the formal definition of a derivative.
Esto es:// This is
Dadas las funciones g y h, con dominio en R (el conjunto de los números reales), se quiere determinar y aplicar en ejemplos la técnica para derivar la función f definida por f(x)=g(x).h(x).
Given the functions g and h, with dominance in R (the set of real numbers), we want to determine and apply in examples the technique to derive the function f defined by f(x)=g(x).h(x).
Comencemos // Let's start
Sabemos que la derivada de una función f en cualquier punto de su dominio está dada por:// We know that the derivative of a function f at any point in its domain is given by:
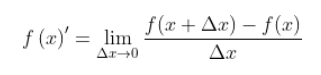
Pero, en nuestro caso particular, f(x) esta definida como un producto de dos funciones g y h, así: f(x)=g(x)/h(x).
But, in our particular case, f(x) is defined as a product of two functions g and h, like this: f(x)=g(x)/h(x).
Por lo tanto, dicha definición adecuada a la definición de f es esta:// Therefore, such a definition appropriate to the definition of f is this:
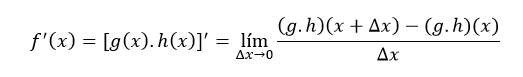
Aplicando la definición de producto de funciones, la expresión anterior queda así:// Applying the definition of a feature product, the above expression looks like this:
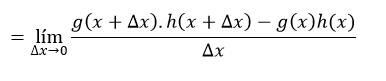
Sumando y restando en el numerador // Adding and subtracting in the numerator g(x+Δx)h(x)
El resultado es este:// The result is this:
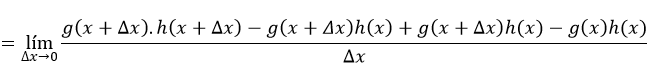
Sacando factor común, va resultando esto:// Finding a common factor, the result is this:
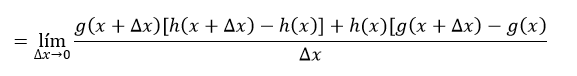
Como g es continua y Δx→0, then: //Since g is continuous and Δx→0, then:
g(x+ Δx)=g(x)
De tal manera, que nuestra expresión toma la siguiente forma:// Thus,our expression takes the following form:
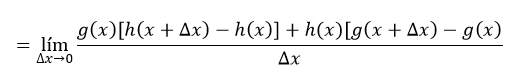
Separando en suma de fracciones y aplicando los teoremas de límites, nos queda así:// Separating the sum of fractions and applying the limit theorems,we get as follows:
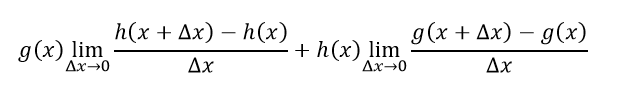
Lo cual se reduce a:// Which boils down to:
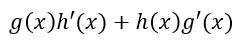
De donde:// Where from:
Lo cual, es la fórmula que estábamos buscando. // Which, is the formula we were looking for.
¿Cómo se aplica esta fórmula? // How is this formula applied?
Veamos un ejemplo:// Let's look at an example:
Hallar la derivada de:// Find the derivative of:
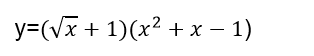
Aquí se nos está solicitando que derivemos a la función ''y'', la cual es el producto de dos funciones, ellas son:
Here we are being asked to derive the function ''y'', which is the product of two functions, which are:
La primera función es √x+1 y la segunda es (x2+x-1) // The first function is √x+1 and the second is (x2+x-1)
Ahora, vamos a aplicar la fórmula, en tal sentido, derivemos la primera de las funciones.// Now, let's apply the formula, in that sense, let's derive the first of the functions.
Es decir, (√x+1)', cuyo resultado es:// That is,(√x+1)', the result of which is: 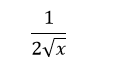
Y luego, la segunda: (x2+x-1)', cuyo resultado es:// And then the second one: ( x2+x-1)', the result of which is: 2x+1
Sustituyamos estos resultados en la fórmula de la derivada de un producto:// Let's substitute these results into the formula of the derivative of a product:
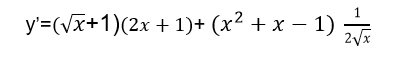
De donde:// Where from:
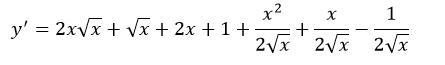
Lo cual es el resultado deseado:// Which is the desired result:
A continuación, dejo algunas actividades para el lector, cualquier duda puede ser planteada a través de los comentarios, con gusto responderé.
Below, I leave some activities for the reader, any questions can be raised through the comments, I will gladly answer.
Hallar la derivada de:// Find the derivative of:
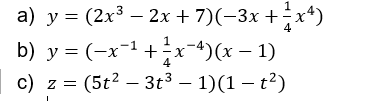

Créditos
El texto es original de la autora, la image es de Pixabay.
Credits
The text is original by the author, the image is from Pixabay.