Este post lo vamos a dedicar a una operación con funciones que recibe el nombre de Función Compuesta, esta operación consiste en aplicar una función a otra función, por ejemplo, si queremos aplicar la función f(x)= x2 a la función g(x)= x +1, significa que debemos hallar esto: f(g(x).
This post is going to be dedicated to an operation with functions called Composite Function, this operation consists of applying a function to another function, for example, if we want to apply the function f(x)= x2 to the function g(x)= x +1, it means that we must find this: f(g(x).
Para hallar f(g(x) seguimos la definición de f que es la función que distinguimos como externa, y siguiendo la lógica en el razonamiento, g(x) será la función interna; de tal forma que aplicamos la función externa sobre la función interna así:
To find f(g(x) we follow the definition of f which is the function we distinguish as external, and following logic in reasoning, g(x) will be the internal function; so we apply the external function to the internal function as follows:
| f(g(x)=f(x+1)= (x +1) 2 = x2 +2x+1 |
También podemos hacer lo contrario, es decir, aplicar g sobre f, ahora, se trata de que la función externa es g y la interna es f, esto es: g(f)x)=g(x2 )= x2 +1.
We can also do the opposite, i.e. apply g on f, now it is that the external function is g and the internal function is f, that is: g(f)x)=g(x2 )= x2 +1.
Para poder identificar el orden de la composición debemos tener una notación adecuada y en tal sentido estas son las notaciones formales para la composición de funciones f y g cualesquiera:
In order to identify the order of the composition we must have an adequate notation and in this sense these are the formal notations for the composition of any f and g functions.
(fog)(x)=f(g(x)) que se lee g compuesta con f y (gof)(x)=g(f(x)) que se lee f compuesta con g.
(fog) (x)=f(g(x)) that you read g compound with f and (gof)(x)=g(f(x)) that you read f compound with g.
Es importante destacar que en la composición de g con f, g debe estar en el dominio de f, y en la composición de f con g, f deberá estar en el dominio de g.
It is important to note that in the composition of g with f, g must be in the domain of f, and in the composition of f with g, f must be in the domain of g.
Veamos un ejemplo de aplicación:
Let's look at an application example:
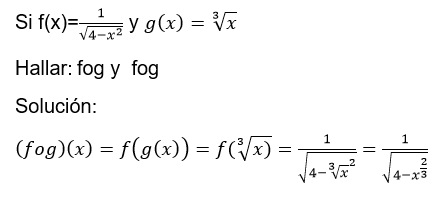
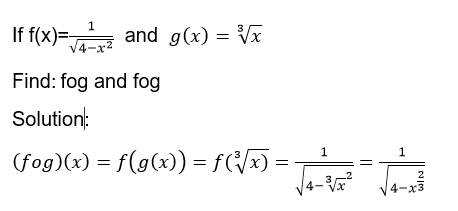
El lector interesado se dará cuenta que esta función resultante de la composición de g con f no está definida para x=8 y para x= -8 ya que, si la evaluamos, por ejemplo, en x=8 se nos presenta una indefinición:
The interested reader will realize that this function resulting from the composition of g with f is not defined for x=8 and for x= -8 since, if we evaluate it, for example, at x=8 we are presented with an indefiniteness:
Veamos:
Let's see:
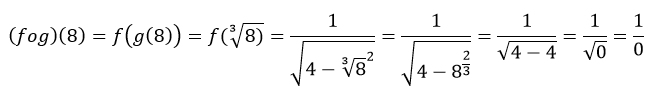
Es claro que este resultado no existe como número real.
It is clear that this result does not exist as a real number.
Lo mismo va a ocurrir con x=-8.
The same thing is going to happen with x=-8.
Recordemos que en el post anterior obtuvimos el dominio de estas dos funciones:
Let's remember that in the previous post we got the mastery of these two functions:
Para hallar el dominio de f, resolvimos esta ecuación cuadrática
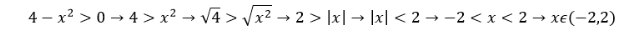
Por lo tanto: Dom(f)= (-2,2)
En el caso de g que está definida por una raíz cúbica, el Dom(g)=R.
To find the domain of f, we solved this quadratic equation
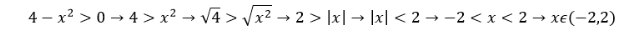
Therefore: Dom(f)= (-2,2).
In the case of g which is defined by a cube root, Dom(g)=R.
Visto esto, las condiciones que debe cumplir g para estar en el dominio de f son las siguientes:
In view of this, the conditions that g must meet in order to be in the domain of f are as follows:
Primero, debemos concentrar la idea de que g(x) debe estar en el dominio de f(x), es decir: g(x) debe pertenecer al intervalo (-2,2).
First, we must concentrate the idea that g(x) must be in the domain of f(x), i.e., g(x) must belong to the interval (-2,2).
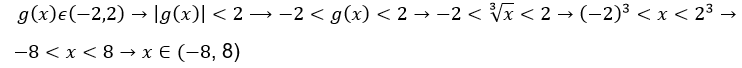
Consecuentemente, el dominio de (fog)(x) consiste en todos los valores de x en el intervalo (-8, 8), con lo cual resolvemos el problema planteado.
Consequently, the domain of (fog)(x) consists of all the values of x in the interval (-8, 8), which solves the problem.
