Hi there. Here is a short guide on unit vectors in mathematics.
Vectors Review
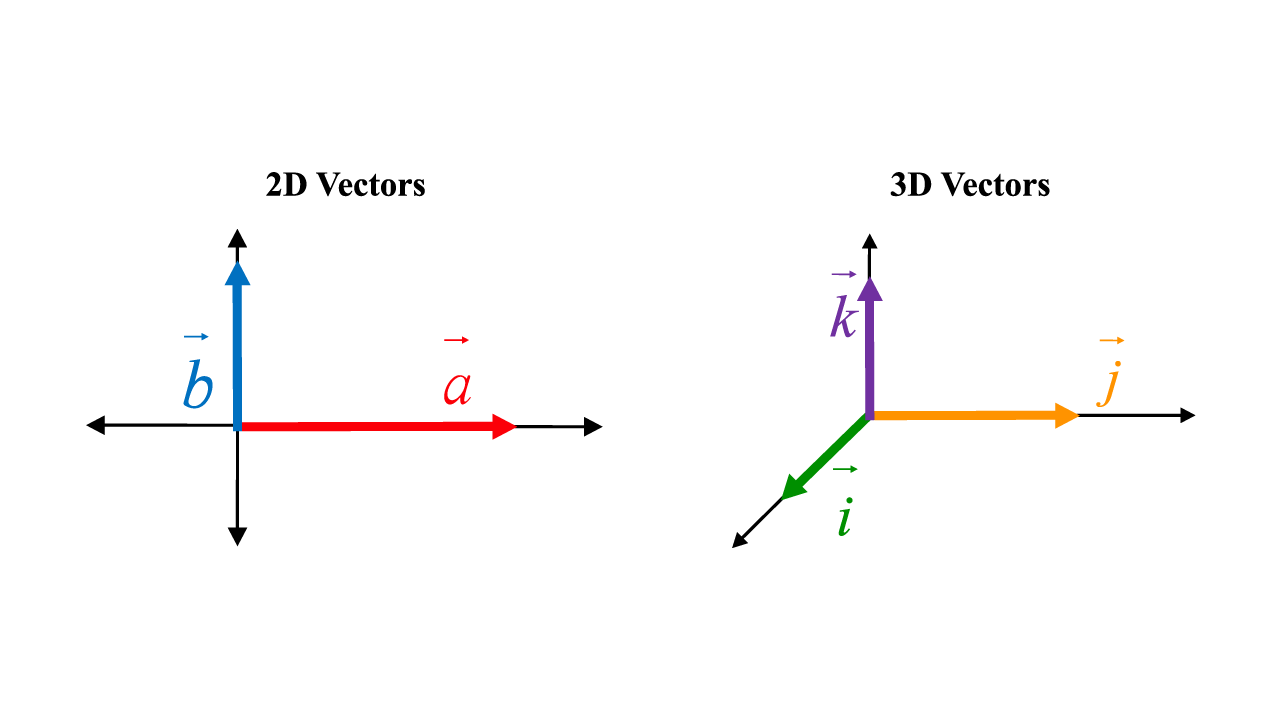
A vector in the geometry and linear algebra framework has a magnitude (or length) and direction. The visual representation is given by a line segment. (Cuemath image source.)

Each vector has a tail as the start and the head as the end.
In terms of writing vectors I prefer using triangle brackets like
You could also use column vectors. The vector <-1, 2> would be
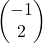
Unit Vectors
Unit vectors have a distance/magnitude of 1. In two dimensions, the unit vectors are:
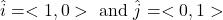
For the unit vector <1, 0>, it means go right 1 unit and move up/down 0 units. With <0, 1>, just move 1 unit up in the y-direction.
When you add a third dimension, you include the height represented by z. The unit vectors are:
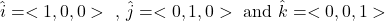
Vectors Applications
The concept of unit vectors is simple. The more complex topics in vectors are needed in order to reach a good level of skill to do applications.
Real life applications of vectors include:
- Physics - Velocity, Forces On Objects, Electromagnetism
- Engineering - Tension, Compression, Circuits, Signals
- Computer Graphics
- Navigation & GPS Systems
- Aerospace & Aviation
Thank you for reading.