
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

02-10-2025-Materials Technologies - Associated Natural Gas [EN]-[IT] With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic in question. (lesson/article code: EX_LZ_20)
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction Gaseous fuels are defined as substances that are in a gaseous state at room temperature and pressure and can burn in the presence of oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat. Typically, these substances are hydrocarbons, compounds composed of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H). For example, methane, which has the chemical formula CH4, or propane, which has the chemical formula C3H8. The main characteristics of gaseous fuels are that they are highly reactive as they mix easily with oxygen and have a high calorific value.
Natural Gas Natural gas is a mixture of combustible gases that forms naturally underground. It is formed by the anaerobic decomposition of organic material that occurred millions of years ago under high pressure and temperature. Natural gas is one of the main fossil energy sources used in the modern world. Natural gas is a tradable commodity, just like gold, oil, or wheat. As of September 2025, natural gas was worth approximately $2.97 per MMBtu (Million British Thermal Units).
Chemical composition of natural gas
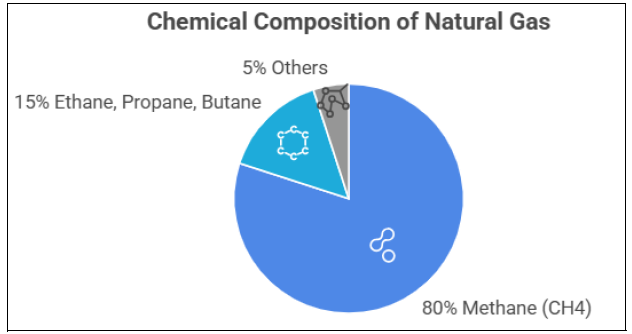
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Napkin.ai
Natural gas is composed of: - approximately 80% of natural gas is methane (CH4) - ethane, propane, and butane are also present in smaller quantities - other components present in even smaller quantities are carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and noble gases.
Associated and Non-Associated Natural Gas When we talk about natural gas, we must actually distinguish between two types: associated natural gas and non-associated natural gas. The difference between the two types is the presence or absence of oil in the extraction field. Below are the two definitions to better clarify the differences between the two.
Associated Natural Gas This is the gas found dissolved or in contact with oil within the deposits, and when crude oil is extracted, the gas is also released. Non-Associated Natural Gas Non-associated natural gas, on the other hand, is found in independent deposits, meaning where the gas is present in pure form, without significant quantities of oil.
**Currently, the largest non-associated natural gas deposits are located in Iran, Qatar, and Western Siberia (Russia).
Natural Gas Purification Treatments One of the questions we might ask is that while natural gas is immediately ready for use once extracted, unfortunately it is not. When extracted, natural gas contains impurities such as water, dust, sulfur, and carbon dioxide, substances that require purification. Therefore, before being ready for use, natural gas undergoes the following purification treatments: - Removal of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) - Reduction of CO2 - Removal of water - Removal of impurities All of this ensures that natural gas, in addition to being ready for use, also meets a quality and safety standard for transportation and use.
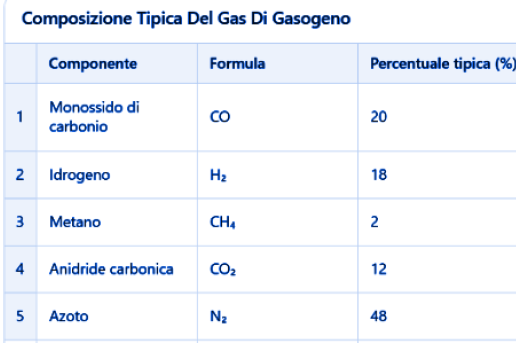
Generator Gas Generator gas, also called lean gas, is a combustible gas obtained from the incomplete combustion of coal, wood, or other carbon-rich solid materials in the presence of air and water vapor. Below is a table of the typical composition of gaseous fuel.
Gaseous fuel was widely used as a fuel for industrial engines and furnaces. Today, it is no longer used in engines, but its concept lives on in modern syngas, obtained from biomass and waste. Modern uses of gaseous fuel are linked to sustainability factors.
Conclusions Gaseous fuels are substances with high reactivity, a high calorific value, and a wide flammability range. They are used in home heating systems, cooking, electricity generation (gas turbine power plants), and in industry, especially in welding and chemical processes. Natural gas is not ready for use once extracted; it undergoes purification treatments to make the gas safe, less corrosive, and suitable for transportation and both residential and industrial use.
Question Did you know that the first mention of the discovery of natural gas occurred in England in 1659? Did you know that William Hart dug the first commercial natural gas well in 1821? Did you know that it was Hart who launched the natural gas industry in the United States?

ITALIAN

02-10-2025-Tecnologie dei materiali - Gas naturale associato [EN]-[IT] Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto (codice lezione/articolo: EX_LZ_20)

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione Vengono definiti combustibili gassosi quelle sostanze che si trovano allo stato gassoso a temperatura e pressione ambiente e che possono bruciare in presenza di ossigeno, liberando energia sotto forma di calore. Solitamente queste sostanze sono gli idrocarburi, sostanze composte da carbonio (C) e idrogeno (H). Ad esempio il metano, che ha formula chimica CH4, oppure il propano che ha formula chimica C3H8. Le caratteristiche principali dei combustibili gassosi è che sono fortemente reattivi in quanto si miscelano facilmente con l’ossigeno ed hanno un potere calorifico elevato.
Il gas naturale Il gas naturale è una miscela di gas combustibili che si forma in maniera naturale nel sottosuolo. Esso si forma con la decomposizione anaerobica di materiale organico avvenuta milioni di anni fa sotto elevate pressioni e temperature. Il gas naturale è una delle principali fonti di energia fossile utilizzate nel mondo moderno. Il gas naturale è una commodity negoziabile in borsa, proprio come oro, petrolio o grano. A settembre 2025 il gas naturale valeva circa 2,97 USD per MMBtu (Million British Thermal Units)
Composizione chimica del gas naturale

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Napkin.ai
Il gas naturale è composta da: -circa l’80% del gas naturale è metano (CH4) -poi sono presenti in quantità minori Etano, Propano e Butano -poi altri componenti presenti in quantità ancora minori sono l’anidride carbonica (CO2), l’azoto, solfuro di idrogeno (H2S) e gas nobili.
Gas naturale associato e non associato Quando parliamo di gas naturale dobbiamo in realtà distinguere tra due tipologie: il gas naturale associato e il gas naturale non associato. La differenza tra le due tipologie è la presenza o meno del petrolio nel giacimento di estrazione. Qui di seguito le due definizioni per chiarire meglio le differenze tra i due.
Gas naturale associato Questo è il gas che si trova disciolto o in contatto con il petrolio all’interno dei giacimenti e quando si estrae il greggio, insieme ad esso si libera anche il gas. Gas naturale non associato Il gas naturale non associato, invece, si trova in giacimenti indipendenti, cioè dove il gas è presente in forma pura, senza significative quantità di petrolio. Attualmente i più grandi giacimenti di gas naturale non associato si trovano in Iran, Qatar e in Siberia occidentale (Russia)
I trattamenti di depurazione del gas naturale Una delle domande che ci possiamo fare è proprio quella che se il gas naturale una volta estratto è subito pronto all’uso, purtroppo no. Il gas naturale, quando viene estratto, contiene impurità come acqua, polveri, zolfo, anidride carbonica, sostanze che richiedono un processo di depurazione. Quindi il gas naturale, prima di essere pronto all’uso, subisce dei trattamenti di depurazione che sono i seguenti: -eliminazione dell’idrogeno solforato (H2S) -riduzione della CO2 -viene tolta l’acqua -vengono tolte le impurità Tutto questo porta il gas naturale, oltre ad essere pronto all’uso, anche ad uno standard di qualità e sicurezza per il trasporto e l’utilizzo.
Gas di gasogeno Il gas di gasogeno, chiamato anche gas povero, è un gas combustibile ottenuto dalla combustione incompleta di carbone, legna o altri materiali solidi ricchi di carbonio in presenza di aria e vapore acqueo. Qui di seguito una tabella della composizione tipica del gas gasogeno

Il gas gasogeno veniva molto usato come combustibile per motori e forni industriali. Esso oggi non si usa più nei motori, ma il suo concetto rivive nel moderno syngas ottenuto da biomasse e rifiuti. Gli impieghi moderni del gas gasogeno sono legati a fattori di sostenibilità.
Conclusioni I combustibili gassosi sono sostanze che hanno un’alta reattività, un potere calorifico elevato ed un ampio campo di infiammabilità. Vengono usati in sistemi di riscaldamento domestico, nella cottura dei cibi, nella produzione di energia elettrica (centrali turbogas) e nell’ambito industriale soprattutto nelle attività di saldatura e processi chimici. Il gas naturale non è pronto all’uso una volta estratto, ma subisce dei trattamenti di depurazione che servono a rendere il gas sicuro, meno corrosivo e adatto al trasporto e all’uso sia civile che industriale
Domanda Sapevate che la prima volta che si fa menzione alla scoperta del gas naturale è nel 1659 in Inghilterra? Sapevate che fu William Hart a scavare il primo pozzo commerciale di gas naturale, esattamente nel 1821? Sapevate che fu proprio Hart a far partire l’industria del gas naturale negli Stati Uniti?
THE END