
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

20-09-2025-Mechanical Measurements-Application of Resistance Thermometers [EN]-[IT]
With this post, I would like to provide a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the article. (lesson/article code: EX_68)
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction First, let's define what a resistance thermometer is. A resistance thermometer is a sensor that measures temperature by exploiting the change in electrical resistance of a material as its temperature varies. Below is an image of a resistance thermometer.
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Main characteristics of resistance thermometers
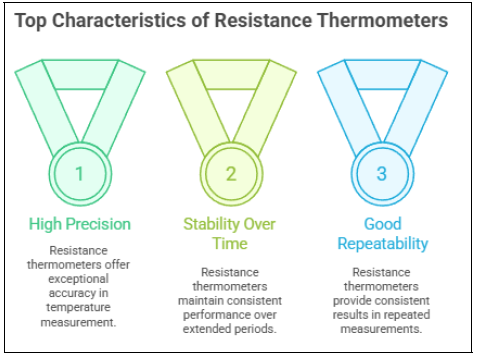
Image created with Artificial intelligence, the software used is Napkin.ai
Resistance thermometers have three main characteristics, meaning three reasons why they are popular: 1- High precision 2- Stability over time 3- Good repeatability
Resistance thermometer applications Resistance thermometers are used in various fields, some of which are described below: Industrial applications Resistance thermometers are used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing plants to regulate the temperature of various environments (such as tanks and pipes) used in these sectors. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) applications Resistance thermometers are also used to regulate the temperature of residential and commercial environments.
Electronics and semiconductors Resistance thermometers are also used to prevent overheating in electronic devices and to perform thermal monitoring of electronic circuits.
Problems with Temperature Measurement with RTDs Resistance thermometers are popular for their high precision, but there are still some issues with temperature measurements with RTDs. We can divide the issues into two broad categories: primary issues and sources of uncertainty. Main issues with temperature measurements with RTDs
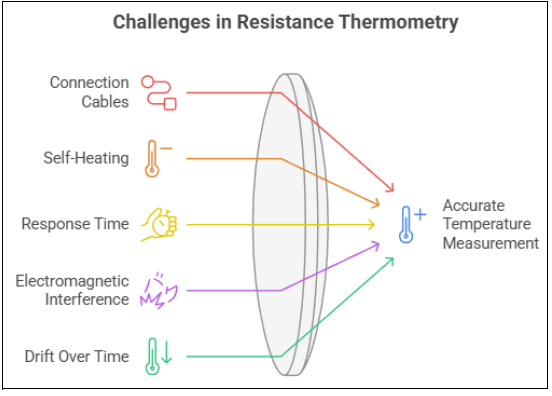
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Napkin.ai
The main issues that can arise when taking temperature measurements with RTDs are the following. 1-Effect of Connection Cables The cables connecting the RTD to the circuit introduce a parasitic resistance that can distort the measurement. 2-Self-Heating The measurement current can cause internal heating. 3-Response Time The response time of a RTD is relatively slow compared to other sensors. 4-Electromagnetic Interference Resistance thermometers are sensitive to electrical noise and electromagnetic interference. 5-Drift Over Time Over time, the RTD can undergo physical or chemical changes, which can alter the calibration curve.
Sources of uncertainty in temperature measurements with resistance thermometers
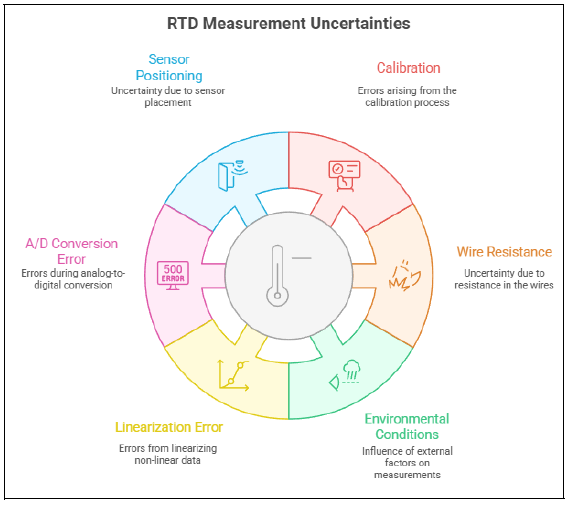
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Napkin.ai
The main sources of uncertainty in resistance thermometer measurements include: 1-Calibration If calibration is not performed correctly, there may be differences between the theoretical and actual sensor curves. 2-Cable Resistance The influence of the resistance of the connecting wires creates measurement uncertainty. 3-Environmental Conditions Humidity, vibrations, and pressure variations can affect the measurement. 4-Linearization Error In these devices, the relationship between temperature and resistance is not perfectly linear. 5-A/D Conversion Error If the signal is digitized, the precision of the converter would affect the accuracy. 6-Sensor Positioning If the RTD is not properly positioned, it may not reflect the true temperature of the point being measured.
Conclusions If we want to take temperature measurements with resistance thermometers, we can say that they represent a reliable and precise solution. However, there are problems such as self-heating, electrical interference, and drift over time. The main sources of uncertainty must be managed with appropriate compensation and calibration techniques. We can say that in applications where precision is more important than response speed, resistance thermometers are still a good choice. Keep in mind that their operating principle, based on the variation of electrical resistance with temperature, allows for stable and repeatable measurements over time.
Question Did you know that the first resistance thermometer, designed with the operating principle we know, was invented by Sir William Siemens in 1871? But did you know that the practical implementation of the device was later carried out by the English physicist Hugh Longbourne Callendar? Did you know that Hugh Longbourne Callendar, also known for his contributions to thermometry and thermodynamics, was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Physics three times (1913, 1918, and 1921), but never won the prize?

ITALIAN

20-09-2025-Misure meccaniche-Applicazione delle termoresistenze [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto (codice lezione/articolo: EX_68)
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione Innanzitutto definiamo cosa è una termoresistenza. Una termoresistenza è un sensore che misura la temperatura sfruttando la variazione di resistenza elettrica di un materiale al variare della temperatura. Qui di seguito un’immagine di una termoresistenza

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Caratteristiche principale delle termoresistenze

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Napkin.ai
Le termoresistenze hanno tre caratteristiche principali, cioè tre motivi per cui possono essere scelte: 1-elevata precisione 2-stabilità nel tempo 3-buona ripetibilità
Applicazioni delle termoresistenze Le termoresistenze vengono usate in diversi ambiti, qui di seguito ne descrivo qualcuno: Applicazioni industriali Le termoresistenze vengono usate in impianti chimici, farmaceutici e alimentari per regolare la temperatura dei vari ambienti (come serbatoi e tubazioni) utilizzati in questi settori. Applicazioni per HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) Le termoresistenze vengono impiegate anche per regolazione della temperatura degli ambienti residenziali e commerciali.
Elettronica e semiconduttori Le termoresistenze vengono usate anche per evitare surriscaldamenti nei dispositivi elettronici e per effettuare controlli termici di un circuito elettronico.
Problematiche relative alla misura di temperatura con termoresistenze Le termoresistenze sono apprezzate per il fatto che sono molto precise, ma esistono comunque delle problematiche nelle misure di temperature con termoresistenze. possiamo dividere le problematiche in due grandi categorie, le problematiche principali e le fonti di incertezza. Problematiche principali delle misure di temperatura con termoresistenze

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Napkin.ai
Le problematiche principali che si possono avere effettuando delle misure di temperatura con le termoresistenze sono le seguenti. 1-Effetto dei cavi di collegamento I cavi che collegano la termoresistenza al circuito introducono una resistenza parassita che può falsare la misura. 2-Autoriscaldamento La corrente di misura può causare un riscaldamento interno 3-Tempo di risposta Il tempo di risposta di una termoresistenza è relativamente lento rispetto ad altri sensori. 4-Interferenze elettromagnetiche Le termoresistenze sono sensibili a disturbi elettrici e interferenze elettromagnetiche 5-Deriva nel tempo La termoresistenza con il passare del tempo può subire alterazioni fisiche o chimiche con la conseguenza che possa essere modificata la curva di calibrazione.
Fonti di incertezza delle misure di temperatura con termoresistenze

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Napkin.ai
Le principali fonti di incertezza nella misura con termoresistenze includono: 1-Calibrazione Se non c’è una corretta calibrazione possono esserci differenze tra la curva teorica e quella reale del sensore. 2-Resistenza dei cavi L’influenza della resistenza dei conduttori di collegamento creano incertezza nella misura 3-Condizioni ambientali L’umidità, le vibrazioni, e le variazioni di pressione possono influenzare la misura 4-Errore di linearizzazione In questi dispositivi la relazione tra temperatura e resistenza non è perfettamente lineare. 5-Errore di conversione A/D Nel caso in cui il segnale venisse digitalizzato, la precisione del convertitore influirebbe sull’accuratezza. 6-Posizionamento del sensore Se la termoresistenza non risultasse essere ben posizionata, potrebbe non riflettere la temperatura reale del punto da misurare.
Conclusioni Se vogliamo effettuare misure di temperatura con termoresistenze possiamo dire che queste rappresentano una soluzione affidabile e precisa, tuttavia esistono delle problematiche come l'autoriscaldamento, le interferenze elettriche e la deriva nel tempo.Le principali fonti di incertezza devono essere gestite con opportune tecniche di compensazione e calibrazione. Possiamo dire che in applicazioni dove la precisione è più importante della velocità di risposta le termoresistenze sono comunque una buona scelta. Teniamo presente che Il loro principio di funzionamento, basato sulla variazione della resistenza elettrica con la temperatura, consente misure stabili e ripetibili nel tempo.
Domanda Sapevate che La prima termoresistenza, pensata con il principio di funzionamento che conosciamo, fu inventata da Sir William Siemens nel 1871? Sapevate però che la realizzazione pratica del dispositivo fu poi eseguita dal fisico inglese Hugh Longbourne Callendar? Sapevate che proprio Hugh Longbourne Callendar, noto anche per i suoi contributi in termometria e termodinamica, fu candidato al Premio Nobel per la fisica per ben tre volte (1913, 1918, e nel 1921), ma non vinse mai il premio?
THE END