~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

26-08-2025 - Operations Research - Knapsack Problem [EN]-[IT] With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic in question. (lesson/article code: MS_01)
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction The knapsack problem is one of the most classic problems in operations research. The knapsack problem is also known as the knapsack problem.
What it says Given a certain number of objects, each with a weight (W) and a value (V), we need to fill a container with a certain capacity (C). We must fill the backpack with the most valuable objects without exceeding the capacity of the container (backpack).
Below is a list of container data:
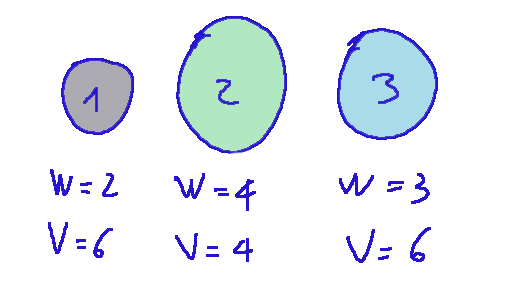
Container 1 W=2 V=6
Container 2 W=4 V=4
Container 1 W=3 V=6
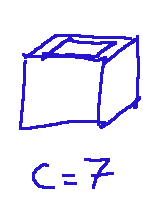
The Backpack The backpack has a capacity of 7, so the sum of the weights of the items (W) cannot exceed 7
The Goal We must maximize the value of the objects, with the constraint that the sum of their weights must not exceed the maximum weight the container can support. In this type of problem, the knapsack problem, we can only decide whether or not to put the object in the knapsack; it cannot be changed. That is, the choice is binary: either we put it in the knapsack or we don't.
Approach What we can do to simply address the Knapsack problem is to create a possibility tree.
Let's start with object 3, then build the tree up to object 1.
Let's consider putting and not putting object 3 in our backpack, and we'll have two possibilities. If we put it in, the container can still hold 4 weight (7-3) and will have a value of 6 (container 3 had a value of V=6). Extending this process to all possibilities is like having an algorithm that grows and displays all the possibilities.
We'll then have this tree:
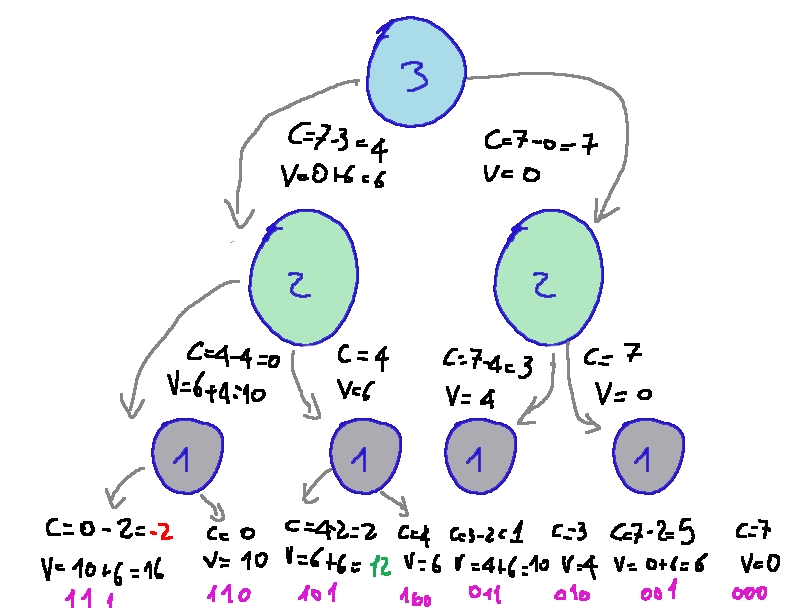
Essentially, this is an intuitive method. In fact, what is the best combination? The one where I have the highest value and don't exceed the capacity of the backpack, that is, combination 101 (purple writing at the bottom of the tree). This combination gives us the value V=12 and the capacity C=2, meaning we're not below zero, which was our weight constraint.
The path that leads us to the optimal solution is shown below.
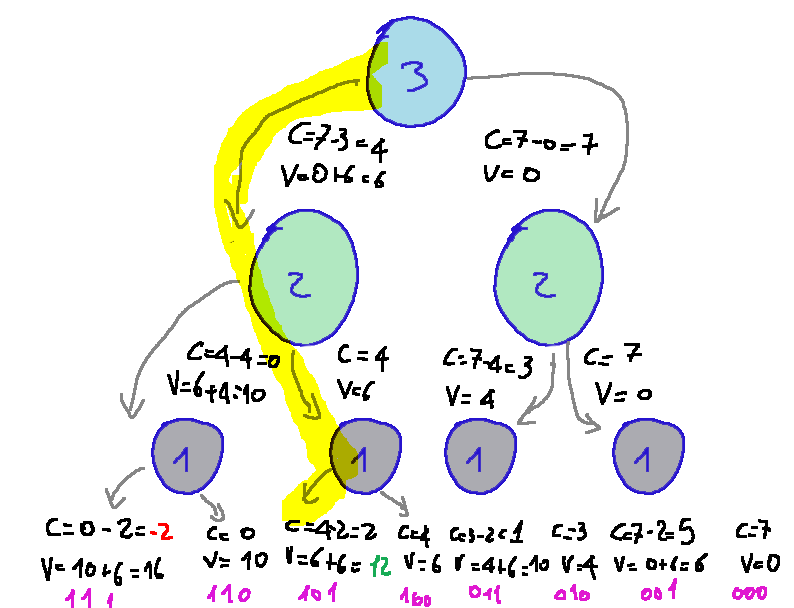
NOTE: If we take the first path on the left, shown below, as an example,
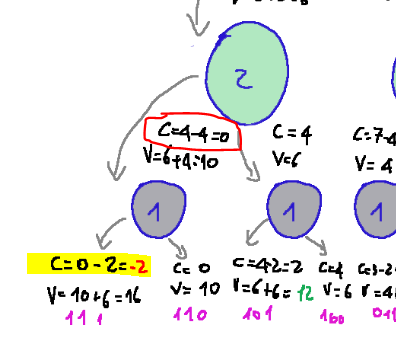
Note that our backpack is already full; in fact, we started with a value of C=4-4=0 (see rectangle (red), if we also add object 1, we will indeed have a value V=16, which is the highest value, but we will overload the knapsack, whereas we should not have exceeded C=7. Indeed, we note that by also adding object 1, we cannot meet the weight constraint, so we cannot consider this solution.
Conclusions The knapsack problem is a mathematical model for deciding how to best use limited resources to maximize an objective. The main applications for solving problems using this method are in logistics, transportation, industrial production, and investment selection.
Question Did you know that there is no clearly identified inventor of the knapsack problem? However, did you know that it was Richard Bellman, an American mathematician, who in the 1950s demonstrated an efficient explanation by presenting it algorithmically?

ITALIAN

26-08-2025 - Ricerca operativa - Problema dello zaino [EN]-[IT] Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto (codice lezione/articolo: MS_01)
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione Il problema dello zaino è uno tra i problemi più classici della ricerca operativo. Il problema dello zaino è conosciuto anche come il problema del problema del knapsack.
Cosa dice Dato un certo numero di oggetti, che hanno sua un peso (W) che hanno un valore (V), bisogna riempire un contenitore con una certa capacità (C). Quello che dobbiamo fare è riempire lo zaino con gli oggetti di maggior valore senza superare la capacità del contenitore (zaino).
Qui di seguito un elenco dati dei contenitori:
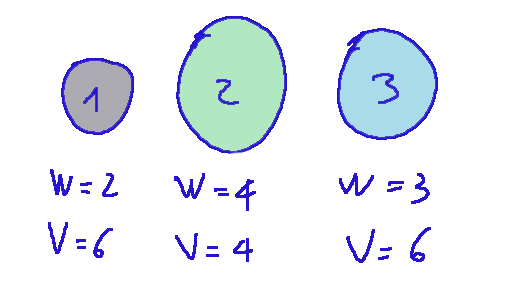
Contenitore 1 W=2 V=6
Contenitore 2 W=4 V=4
Contenitore 1 W=3 V=6
Lo zaino Lo zaino ha una capacità di 7, quindi la somma dei pesi degli oggetti (W) non può superare 7

L'obiettivo Dobbiamo massimizzare il valore degli oggetti con il vincolo che la somma dei loro pesi non devono superare il peso massimo che il contenitore può sopportare. In questa tipologia di problema, cioè nel problema dello zaino, possiamo solo decidere se mettere oppure no l'oggetto, non sono modificabili. Cioè, la scelta è binaria, o lo mettiamo nello zaino, oppure no.
Approccio Quello che possiamo fare per affrontare in maniera semplice il problema dello Knapsack è creare un albero delle possibilità.
Partiamo dall'oggetto 3, poi costruiamo l'albero fino all'oggetto 1.
Consideriamo di mettere e di non mettere nel nostro zaino l'oggetto 3 e avremo due possibilità Se lo mettiamo il contenitore potrà portare ancora 4 di peso (7-3) ed avrà un valore di 6 (il contenitore 3 aveva valore V=6) Estendendo questo processo a tutte le possibilità è come avere un algoritmo che si sviluppa e mostra tutte le possibilità.
Avremo poi questo albero:

Sostanzialmente questo è un metodo intuitivo. Infatti quale risulta essere la combinazione migliore? Quella dove ho il maggior valore e non supero la capacità dello zaino, cioè la combinazione 101 (scritte viola in fondo all'albero). Questa combinazione ci da il valore di V=12 e la capacità C=2, cioè non siamo sotto lo zero, che era il nostro vincolo di peso.
Qui di seguito è indicato il percorso che ci porta alla soluzione ottimale.

NOTA: Se prendiamo come esempio il primo percorso di sinistra, qui sotto riportato

Notiamo che il nostro zaino è già pieno, infatti partivamo con un valore di C=4-4=0 (vedi rettangolo rosso), se aggiungiamo anche l'oggetto 1, avremo si un valore V=16, cioè il valore più alto, ma andiamo a sovraccaricare lo zaino, mentre non dovevamo superare C=7. Notiamo infatti che aggiungendo anche l'oggetto 1, non riusciamo a rispettare il vincolo di peso, quindi non possiamo considerare questa soluzione.
Conclusioni Il problema del knapsack, o probelma dello zaino, è un modello matematico per decidere come usare al meglio risorse limitate massimizzando un obiettivo. Le principali applicazioni per risolvere problemi usando questo metodo sono nella logistica, nei trasporti, nella produzione industriale e nella selezione di investimenti.
Domanda Sapevate che non c'è un ideatore ben identificato per il problema dello zaino (o knapsack problem)? Sapevate però che fu Richard Bellman, matematico statunitense, che negli anni '50 che mostrò una spiegazione efficiente mostrandolo in maniera algoritmica?
THE END