~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH 30-09-2025 - Analytic Geometry - The Identity Matrix [EN]-[IT] With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic mentioned above. (lesson/article code: MS_01)

Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction Today we will try to understand some operations commonly performed in analytic geometry.
The Matrix In analytic geometry, the matrix is a cornerstone of the discipline itself. The matrix is a mathematical tool used to represent geometric data. It can represent points and vectors, and describe geometric transformations and systems of equations.
Standard 2x2 Matrix (General Form)
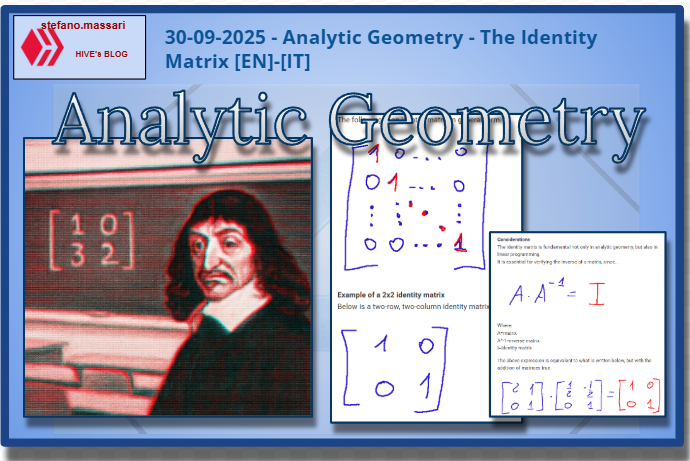
A matrix is composed of n rows and n columns. It contains coefficients, and in the image above, a, b, c, and d are generic coefficients that can represent a geometric transformation.
Example of a 2x2 Matrix Below is an example of a matrix consisting of 2 rows and 2 columns.
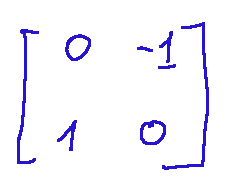
Identity Matrix An identity matrix is a square matrix in which all diagonal elements are equal to 1 and all other elements are equal to 0.
In analytic geometry, the identity matrix represents a transformation that leaves the points or vectors unchanged.
Identity Matrix, General Form The following is an identity matrix in general form.
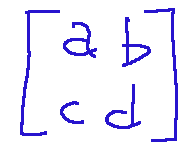
Example of a 2x2 identity matrix Below is a two-row, two-column identity matrix.
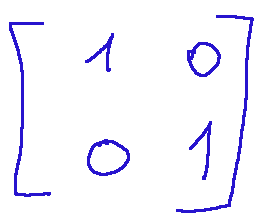
This matrix is a neutral element for 2x2 matrix multiplication. The identity matrix is a general concept in linear algebra and is not specific to a single matrix.
Considerations The identity matrix is fundamental not only in analytic geometry, but also in linear programming. It is essential for verifying the inverse of a matrix, since...
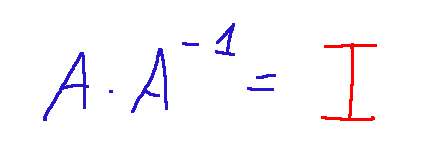
Where: A=matrix A^-1=inverse matrix I=identity matrix
The above expression is equivalent to what is written below, but with the addition of matrices true
Conclusions Analytic geometry can be used to describe geometric figures, solve geometric problems, translate geometric problems into equations, and, above all, it is fundamental to modern computer graphics.
Question Did you know that analytic geometry is used to calculate the orientations and positions of objects in space? Did you know that NASA and other space agencies use matrices based on analytic geometry to model the trajectories of satellites and probes? Did you know that René Descartes (1596-1650), also known as Descartes, is generally considered the father of analytic geometry?

[ITALIAN] 30-09-2025 - Geometria analitica - La matrice identità [EN]-[IT] Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto (codice lezione/articolo: MS_01)

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione Oggi proveremo a comprendere qualche operazione che si esegue solitamente in geometria analitica.
La matrice In geometria analitica la matrice è un pilastro della disciplina stessa. La matrice è uno strumento matematico utilizzato per rappresentare dati geometrici. Può rappresentare punti e vettori, può descrivere trasformazioni geometriche e sistemi di equazioni.
Matrice 2x2 standard (forma generale)

Una matrice è composta da n righe e n colonne. Al suo interno presenta i coefficienti e nell'immagine sopra a, b, c, d, sono coefficienti generici che possono rappresentare una trasformazione geometrica.
Esempio di matrice 2x2 Qui di seguito un esempio di una matrice formata da 2 righe e 2 colonne.
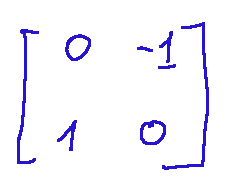
Matrice identità Una matrice identità è una matrice quadrata in cui tutti gli elementi della diagonale sono uguali a 1 e tutti gli altri sono uguali a 0. In geometria analitica, la matrice identità rappresenta una trasformazione che lascia invariati i punti o i vettori.
Matrice identità, forma generale Qui di seguito è rappresentata una matrice identità in forma generale.

Esempio di matrice identità 2x2 Qui di seguito è rappresentata una matrice identità di due righe e due colonne.
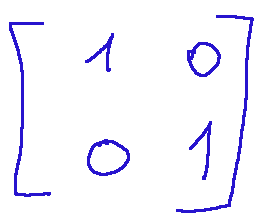
Questa matrice è un l'elemento neutro per la moltiplicazione di matrici 2x2. La matrice identità è un concetto generale in algebra lineare e non è specifica di una singola matrice.
Considerazioni La matrice identità è fondamentale non sono in geometria analitica, ma anche nell'ambito della programmazione lineare. Essa è fondamentale per verificare l'inverso di una matrice, poiché ...
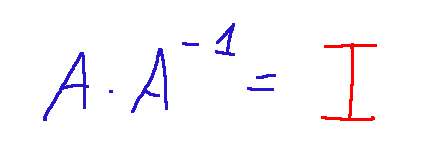
Dove: A=matrice A^-1=matrice inversa I=matrice identità
L'espressione sopra riportata equivale a ciò che è scritto sotto inserendo però delle matrice vere
Conclusioni Con la geometria analitica si possono descrivere figure geometriche, risolvere problemi geometrici, tradurre problemi geometrici in equazioni, ma soprattutto è fondamentale per la moderna per la computer grafica.
Domanda Sapevate che la geometria analitica è usata per per calcolare orientamenti e posizioni di oggetti nello spazio? Sapevate che la NASA e altre agenzie spaziali usano matrici basate sulla geometria analitica per modellare le traiettorie dei satelliti o delle sonde? Sapevate che René Descartes (1596-1650), conosciuto anche come Cartesio, è generalmente considerato il padre della geometria analitica?
THE END